I have taken what Paul described into a working example of my own using Content Negotiation with Spring MVC Rest support.
http://spring.io/blog/2013/05/11/content-negotiation-using-spring-mvc
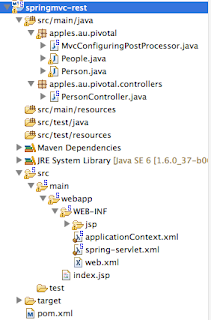
The project I created looks as follows
The complete code for this example exists on GitHub as follows
https://github.com/papicella/SpringMVCRest-ContentNegotiation
1. Create the required pom.xml dependancy elements as shown below.
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>springmvc-rest</groupId>
<artifactId>springmvc-rest</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<properties>
<spring.version>3.2.4.RELEASE</spring.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.codehaus.jackson</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-mapper-asl</artifactId>
<version>1.9.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.xml.bind</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb-api</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.xml</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb-impl</artifactId>
<version>2.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
2. Create a Person class as follows
Person.java
package apples.au.pivotal;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlRootElement
public class Person implements Serializable
{
private int id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
public Person()
{
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Person(int id, String firstName, String lastName) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [id=" + id + ", firstName=" + firstName + ", lastName="
+ lastName + "]";
}
}
3. Create a People class which provides a list of Person objects, we do this so we can return XML as a List doesn't work directly with JAXB
People.java
package apples.au.pivotal;
import java.util.List;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlRootElement(name="people")
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class People
{
private List<Person> people;
protected People() {} // Keep JAXB happy
public People(List<Person> people)
{
this.people = people;
}
@XmlElement(name="person")
public List<Person> getPeople()
{
return people;
}
}
4. Create a controller as follows, there is a request mapping for HTML as well here with the same path, which is the default, in order not to duplicate code we call the JSON/XML method from the HTML method itself.
PersonController.java
package apples.au.pivotal.controllers;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import apples.au.pivotal.People;
import apples.au.pivotal.Person;
@Controller
public class PersonController
{
private static List<Person> personList;
static
{
personList =
Arrays.asList(new Person[]
{ new Person(1, "Pas", "Apicella"),
new Person(2, "Lucia", "Apicella"),
new Person(3, "Lucas", "Apicella"),
new Person(4, "Siena", "Apicella")
});
}
@RequestMapping(value="/people",
method = RequestMethod.GET,
produces={"application/xml", "application/json"})
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public @ResponseBody People listWithJSON()
{
return new People(personList);
}
// View-based method
@RequestMapping(value = "/people", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String listWithView(Model model, HttpServletResponse response, HttpServletRequest request)
{
// Call RESTful method to avoid repeating code
model.addAttribute("peopleList", listWithJSON().getPeople());
// Return the view to use for rendering the response
return "people";
}
}
5. Create a Spring XML file as follows
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd">
<!-- Activates various annotations to be detected in bean classes -->
<context:annotation-config />
<!-- Scans the classpath for annotated components that will be auto-registered as Spring beans.
For example @Controller and @Service. Make sure to set the correct base-package-->
<context:component-scan base-package="apples.au.pivotal.controllers" />
<!-- Configures the annotation-driven Spring MVC Controller programming model.
Note that, with Spring 3.0, this tag works in Servlet MVC only! -->
<bean id="cnManager"
class="org.springframework.web.accept.ContentNegotiationManagerFactoryBean">
<property name="favorPathExtension" value="true"/>
<property name="ignoreAcceptHeader" value="true" />
<property name="defaultContentType" value="text/html" />
<property name="useJaf" value="false"/>
<property name="mediaTypes">
<map>
<entry key="html" value="text/html" />
<entry key="json" value="application/json" />
<entry key="xml" value="application/xml" />
</map>
</property>
</bean>
<mvc:annotation-driven content-negotiation-manager="cnManager"/>
<bean class="apples.au.pivotal.MvcConfiguringPostProcessor" />
</beans>
6. Create a class to enable pretty print for JSON data
MvcConfiguringPostProcessor.java
package apples.au.pivotal;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJacksonHttpMessageConverter;
/**
* The HTTP Message converters are created automatically by Spring. To perform
* additional configuration we use a bean post-processor.
*/
public class MvcConfiguringPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Enable pretty print on any bean of type
* {@link MappingJacksonHttpMessageConverter} or
* {@link MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter}.
*/
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String name) throws BeansException
{
if (bean instanceof HttpMessageConverter<?>)
if (bean instanceof MappingJacksonHttpMessageConverter) {
((MappingJacksonHttpMessageConverter) bean).setPrettyPrint(true);
}
else if (bean instanceof MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter) {
((MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter) bean).setPrettyPrint(true);
}
return bean;
}
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException
{
// Nothing to do
return bean;
}
}
7. Finally create a HTML view page
people.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Spring MVC Rest Demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Spring MVC Rest Demo</h2>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>Id</th>
<th>First Name</th>
<th>Last Name</th>
</tr>
<c:forEach var="row" varStatus="loop" items="${peopleList}">
<tr>
<td>${row.id}</td>
<td>${row.firstName}</td>
<td>${row.lastName}</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
<p />
Created by Pas Apicella
</body>
</html>
8. Run the application and access the 3 supported views with request mapping path of "/people"
HTML - http://localhost:8080/springmvc-rest/apples/people
JSON - http://localhost:8080/springmvc-rest/apples/people.json
XML - http://localhost:8080/springmvc-rest/apples/people.xml



3 comments:
Great....thanks
Thanks, nice instruction
Finally I understand this thanks to your post!
Post a Comment